Introduction
Diabetes: A Menacing Modern Epidemic
Diabetes, a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels, has emerged as a formidable global health challenge. With an estimated 463 million adults affected worldwide, diabetes not only imposes significant physical and emotional burdens but also leads to serious complications such as cardiovascular diseases, kidney failure, and vision impairment. As such, effective management of diabetes is of paramount importance for individuals striving to lead healthy lives.
The Crucial Role of Diet in Diabetes Management
When it comes to controlling diabetes, the significance of dietary choices cannot be overstated. A thoughtfully crafted diet can regulate blood sugar levels and even reduce the risk of developing complications associated with this condition.
By adopting an appropriate diet plan, individuals with diabetes can gain greater control over their health outcomes and improve their overall quality of life. Among the various dietary approaches available, two have garnered considerable attention—the Ketogenic or Keto and Mediterranean diets for Diabetes.
An Introduction to the Keto Diet
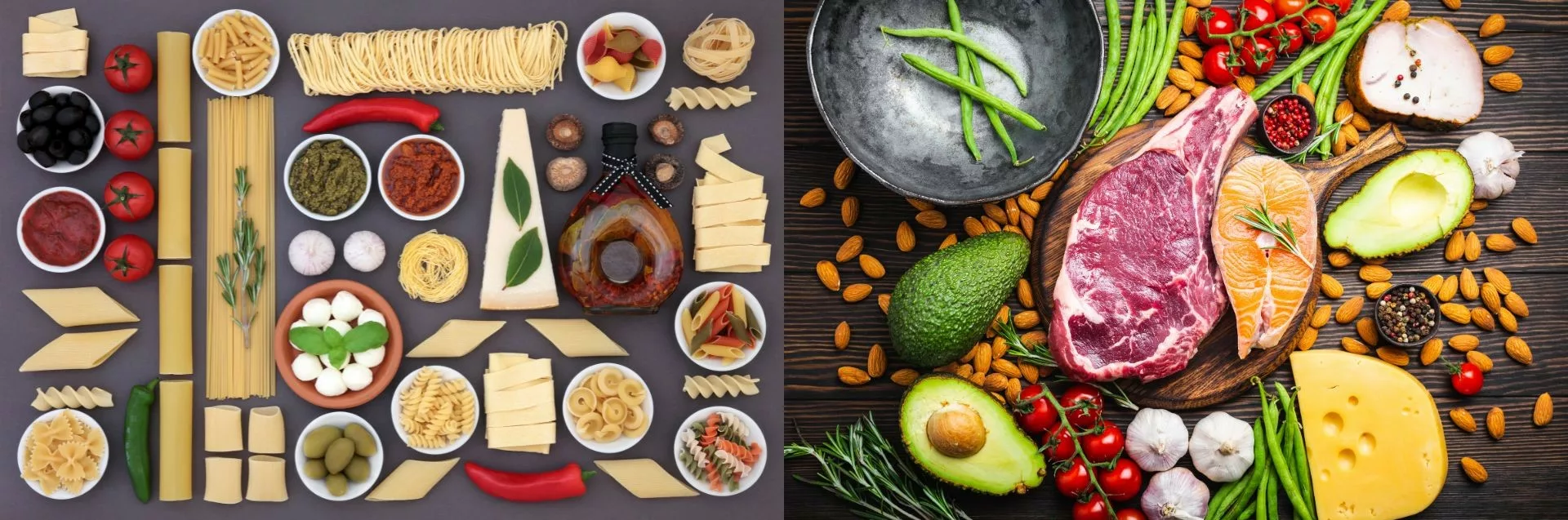
The Keto diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat eating plan that aims to induce a state of ketosis in the body. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake while increasing fat consumption moderately and maintaining moderate protein intake, this diet prompts the body to break down stored fats for energy instead of relying on glucose derived from carbohydrates. This metabolic shift not only aids in weight loss but also has potential benefits for managing diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity.
The Mediterranean Diet: A Celebration of Wholesome Eating
Contrasting with the strictness of the Keto diet is the Mediterranean diet—a flexible and balanced approach that emphasizes whole foods rich in fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, lean proteins like fish and poultry, healthy fats such as olive oil and nuts—particularly walnuts—and moderate consumption of dairy products. Rooted in the eating habits of countries bordering the Mediterranean Sea, this diet has garnered attention for its health benefits, including reduced risk of chronic diseases like diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers.
Choosing Between Keto and Mediterranean: A Matter of Personalization
Selecting the optimal dietary approach to manage diabetes can be a perplexing decision. While both Keto and Mediterranean diets have shown promise in various studies, it is crucial to consider individual factors such as personal preferences, metabolic health, cultural background, and lifestyle.
Exploring the intricacies of these two diets will provide valuable insight into how they affect blood sugar control and overall well-being. Join us as we journey through the unique characteristics and potential benefits of both the Keto and Mediterranean diets for individuals with diabetes.
Intriguingly distinct yet united by their potential to empower individuals with diabetes in managing their condition effectively, the Keto and Mediterranean diets stand at opposite ends of the dietary spectrum. By delving deeper into their mechanisms of action, specific benefits, drawbacks, and scientific evidence supporting their efficacy in diabetes management will equip you with the knowledge to make an informed decision about your dietary choices.
This article digs into details of Keto and Mediterranean diets for Diabetes.
Understanding the Keto Diet
The Ketogenic State
The ketogenic state, also known as ketosis, is a metabolic condition that occurs when the body shifts its primary energy source from glucose to ketones. In this state, the liver produces ketones by breaking down fats, which are then used as fuel by the body’s cells. This fundamental shift alters the body’s energy metabolism and has profound effects on various physiological processes.
One significant effect of entering ketosis is improved insulin sensitivity. When carbohydrates are restricted in a ketogenic diet, blood sugar levels stabilize and insulin production decreases.
Reduced insulin levels lead to enhanced insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to utilize glucose more efficiently. This benefit is particularly crucial for individuals with diabetes since it helps regulate blood sugar levels and reduces reliance on exogenous insulin.
A Nutrient Symphony: Composition of a Typical Keto Diet
A well-designed keto diet primarily consists of high fat, moderate protein, and low carbohydrate intake. The macronutrient composition is meticulously balanced to induce and sustain ketosis while providing adequate nourishment for optimal health.
Fat takes center stage in a keto diet, constituting approximately 70-80% of total daily calorie intake. Sources of healthy fats include avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds, while saturated fats from sources like coconut oil or grass-fed butter are also embraced due to their unique properties in promoting ketosis.
Protein plays a supporting role in the ketogenic symphony. Consuming moderate amounts (around 20-25% of total calories) ensures adequate amino acids for muscle maintenance without hindering ketone production.
High-quality protein sources such as eggs, fish, poultry, and grass-fed meats are commonly recommended. Carbohydrates take a backseat on this dietary journey but should not be completely eliminated (usually less than 10% of total calories).
The aim is to restrict intake to non-starchy vegetables, leafy greens, and low-carb fruits. This approach minimizes blood sugar spikes and keeps the body in a steady state of ketosis.
The Mechanism of Action
The keto diet offers a unique mechanism of action that can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes. By drastically reducing carbohydrate intake, the body’s dependency on glucose decreases, resulting in improved glycemic control and reduced insulin requirements. In ketosis, blood sugar levels tend to stabilize at lower levels due to the limited availability of glucose.
This can mitigate the risk of hyperglycemia and associated complications. Moreover, several studies have shown that following a keto diet may lead to significant weight loss, which is often crucial in managing diabetes as excess weight exacerbates insulin resistance.
Additionally, the ketogenic state enhances lipid metabolism by increasing levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol while reducing triglyceride concentrations. This shift promotes cardiovascular health and reduces the risk factors associated with diabetes-related complications such as heart disease.
Understanding how the ketogenic diet affects the body is essential for comprehending its potential role in diabetes management. Through inducing ketosis and altering metabolic pathways, this high-fat, moderate-protein, low-carbohydrate approach provides unique therapeutic benefits that can help individuals with diabetes achieve better glycemic control while positively impacting overall health markers.
Benefits and Drawbacks of the Keto Diet for Diabetes
Benefits
The Keto diet has gained popularity in recent years due to its potential benefits for individuals with diabetes. One of the key advantages is rapid weight loss, which can have a significant impact on diabetes management. Shedding excess pounds not only improves overall health but also enhances insulin sensitivity, allowing better control over blood sugar levels.
Furthermore, research suggests that following a Keto diet can lead to reduced blood sugar levels and decreased dependency on medication. By severely restricting carbohydrate intake, the body enters a state of ketosis where it becomes highly efficient at burning fat for fuel instead of glucose.
This metabolic shift can result in lower insulin requirements and improved glycemic control. In addition to these benefits, adopting a Keto diet may promote a better lipid profile in individuals with diabetes.
Studies have shown that this dietary approach can increase levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol – often referred to as “good” cholesterol – which plays a crucial role in protecting against heart disease. Improved lipid profiles are particularly important for people with diabetes who are at higher risk of cardiovascular complications.
Drawbacks
While the Keto diet offers several potential benefits for managing diabetes, it is essential to consider its drawbacks as well. One significant challenge relates to the strict dietary restrictions imposed by this eating pattern. The consumption of carbohydrates must be severely limited, making it difficult for some individuals to adhere to the diet long-term.
This strictness can impact social interactions revolving around food and may require careful planning when eating out or attending events. Another concern associated with the Keto diet is the potential risk of nutrient deficiencies due to limited food choices.
With an emphasis on high-fat foods and restricted carbohydrate intake, certain essential nutrients such as fiber, certain vitamins (like vitamin C), and minerals (like potassium) may become deficient if not adequately substituted through careful food selection or supplementation. Therefore, close monitoring and consultation with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian are crucial to ensure nutrient adequacy.
In addition, some individuals may experience side effects during the initial adaptation phase of the Keto diet, commonly known as “Keto flu.” These temporary symptoms may include fatigue, headaches, irritability, and constipation. However, it is important to note that these side effects typically resolve within a few weeks as the body adapts to the new metabolic state.
>>> Check This Resource To Uncover The Science Behind The Ketogenic Diet
Understanding the Mediterranean Diet
Overview of Mediterranean diet principles
The Mediterranean diet is a dietary pattern inspired by the traditional eating habits of countries surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It emphasizes whole foods, fresh ingredients, and a balanced approach to nutrition.
The core principles of this diet include consuming an abundance of plant-based foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. It also encourages moderate consumption of fish and seafood while limiting red meat intake.
Emphasis on whole foods, plant-based ingredients, and healthy fats
One of the key features of the Mediterranean diet is its focus on whole foods and plant-based ingredients. This means prioritizing minimally processed foods that are rich in nutrients and avoiding highly processed products laden with additives.
Fresh fruits and vegetables provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber while contributing to overall health. Furthermore, healthy fats play a crucial role in this eating pattern.
Olive oil – abundant in monounsaturated fats – is a staple in Mediterranean cuisine due to its potential benefits for heart health. Other sources of healthy fats include nuts (such as almonds and walnuts), seeds (like flaxseeds), avocados, and fatty fish (such as salmon) which provide omega-3 fatty acids.
The role of fruits,
Fruits play a significant role in the Mediterranean diet, providing a wide array of essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. They serve as an excellent source of natural sugars and fiber while offering a variety of flavors and textures. The consumption of fruits in their whole form is encouraged over juices or processed fruit products to retain their full nutritional benefits.
Additionally, incorporating a diverse range of colorful fruits into the diet provides potent antioxidants that help combat inflammation and oxidative stress – factors often associated with chronic diseases like diabetes. The Mediterranean diet encourages individuals to enjoy seasonal fruits as part of their daily meals or snacks.
To Summarize
While both the Keto and Mediterranean diets have potential benefits for managing diabetes, it is essential to carefully consider their respective advantages and drawbacks. The Keto diet’s ability to promote rapid weight loss and improve insulin sensitivity can be beneficial for individuals struggling with diabetes.
However, its strict restrictions may pose challenges in long-term adherence, potentially leading to nutrient deficiencies. On the other hand, the Mediterranean diet offers a balanced approach that emphasizes whole foods, plant-based ingredients, and healthy fats.
Its focus on nutrient-dense foods provides essential vitamins and minerals while reducing the risk of nutrient deficiencies associated with more restrictive diets. Choosing between these two dietary approaches should be based on individual preferences, medical advice from healthcare professionals, or registered dietitians specializing in diabetes care.
It is vital to customize dietary recommendations according to an individual’s personal health goals while considering long-term sustainability. When contemplating changes in dietary habits for diabetes management, exploring various options under professional guidance can lead to finding a suitable eating pattern that not only controls blood sugar levels but also promotes overall health and well-being.
References
Prevention and control of type 2 diabetes by Mediterranean diet: A systematic review – ScienceDirect
How the Keto Diet Affects Type 2 Diabetes – Cleveland Clinic